Industrial Carbon Capture
By Mark Brown, WKC Group
What is Industrial Carbon Capture and Storage?
Industrial carbon emissions come from industrial processes and stationary emission sources, such as power stations, cement production and refineries.
Industrial carbon capture and storage involves capturing CO2 at emission sources, transporting, and then storing or burying it in a deep, underground location.
How is Industrial Carbon Dioxide Captured?
CO2 is captured in industrial settings using the following techniques.
Post-combustion – in this technique CO2 is removed after burning fuel
Pre-combustion – in this technique CO2 is trapped before burning fuel
Oxyfuel combustion – in this technique the fuel is burned in oxygen instead of air. This results in almost pure CO2 that can be transported and stored.
How is Industrial Carbon Dioxide Transported?
Pipelines are the primary means of CO2 transport. Ships and road tankers are used for small scale and specialist applications.
How is Industrial Carbon Dioxide Stored?
Industrial CO2 is commonly stored in deep geological formations.
CO2 is converted into a high pressure, liquid-like form known as ‘supercritical CO2’ before being injected directly into deep geological formations. These are commonly sedimentary rocks in old oil or gas fields, but volcanic rocks and saline aquifers are also used. Physical structures prevent CO2 from escaping to the surface. These include impermeable ‘caprocks’ and geochemical trapping mechanisms.
Recent technological advances in industrial carbon capture include graphene production and engineered molecules. Graphene production uses CO2 as a raw material. It is heavily used in the production of tech devices such as smartphones and computer processors. Engineered molecules involve changing the shape of molecules to form new compounds by capturing carbon from the air. It is envisioned that this will be an efficient way of creating raw materials while reducing atmospheric carbon.
Industrial Carbon Capture, Utilisation and Storage (CCUS)
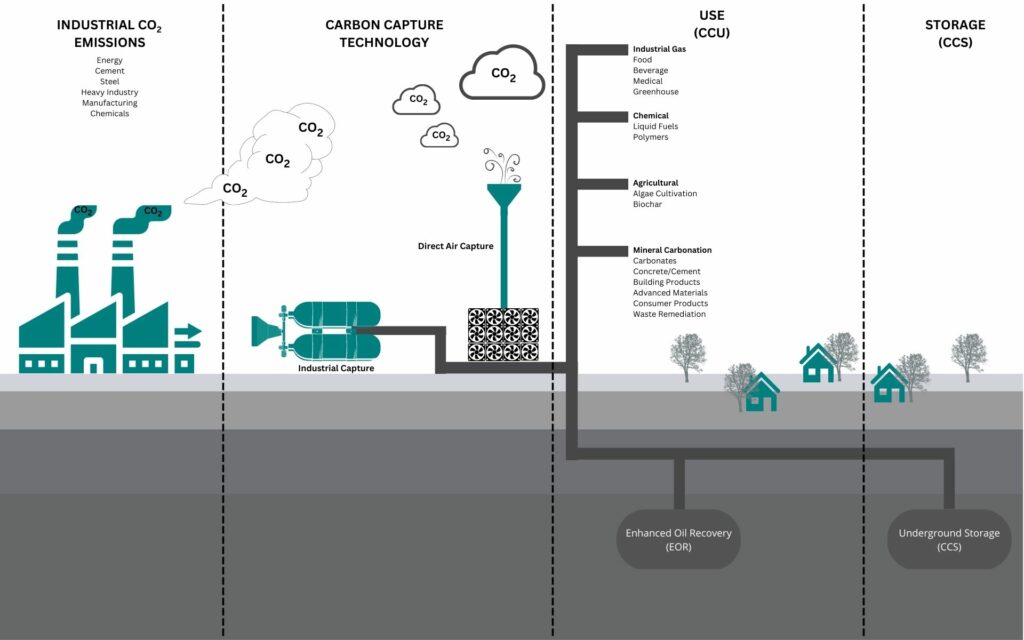 The process of CCUS, figure adapted from Dezeen
The process of CCUS, figure adapted from Dezeen
Conclusion
Advances in technology are enabling carbon to be extracted from industrial activities on an even greater scale.
The simplest way to scaling carbon capture though is to protect and restore our natural environment.

