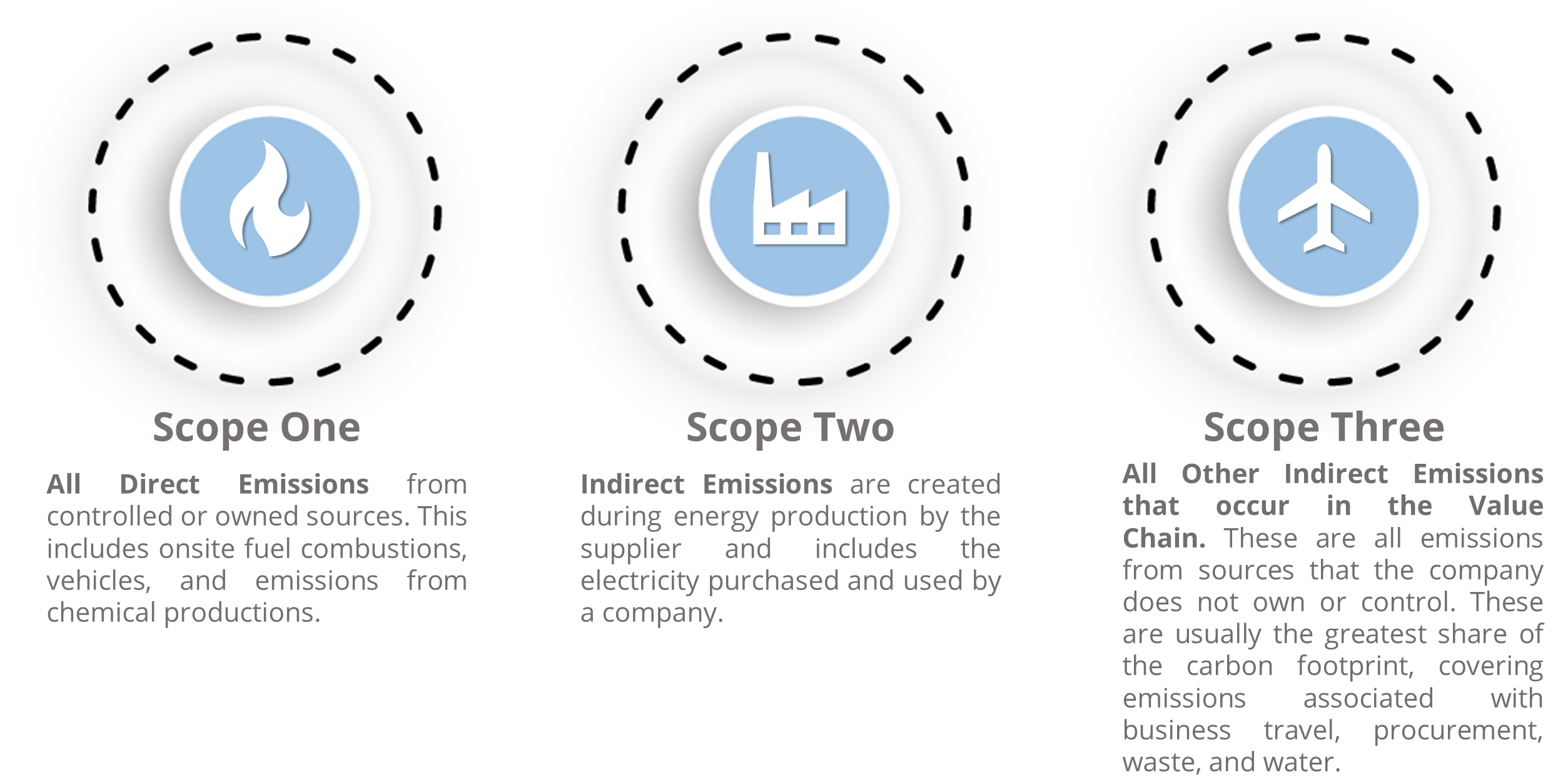
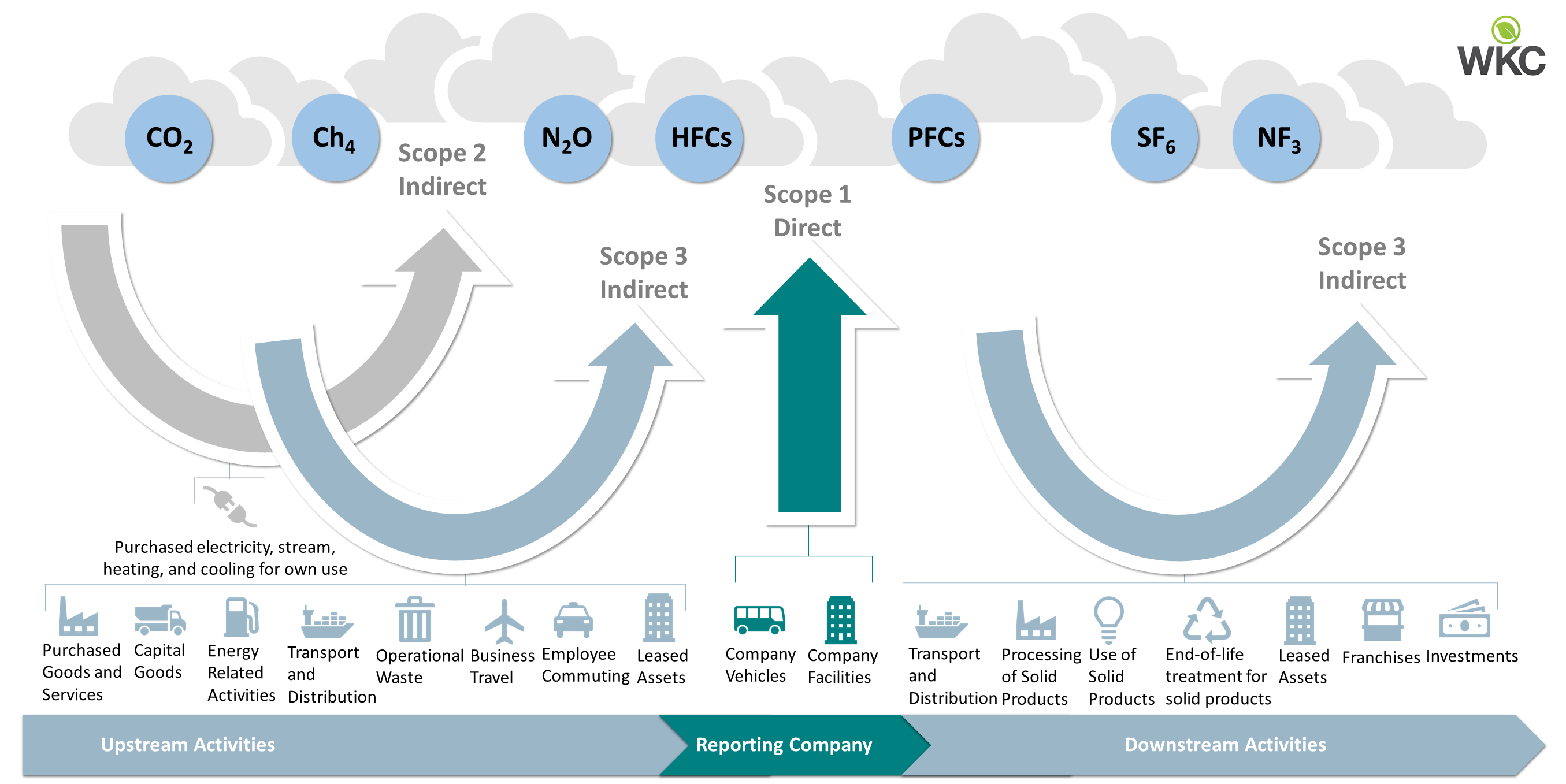
Carbon Capture and Sequestration Services
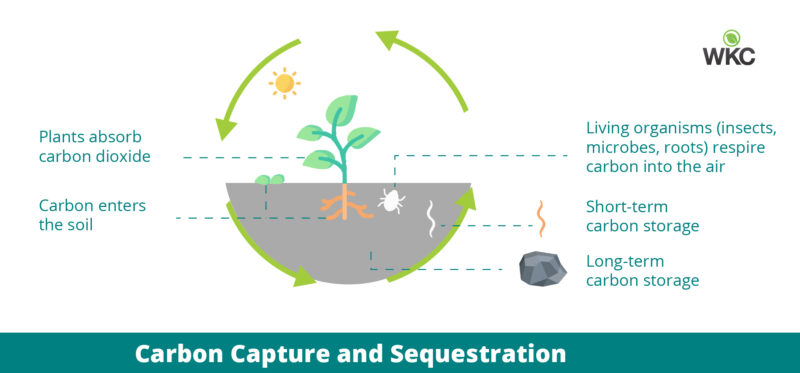
Biological carbon capture and sequestration refers to carbon dioxide (CO2) that is absorbed from the atmosphere and stored within the natural environment.
Carbon capture calculations can be used to estimate how much carbon is captured and stored in this way.
These calculations are important to understand the potential of biological sequestration as a method of offsetting carbon released into the atmosphere through natural and human activities, as well as a method of mitigating climate change by reducing atmospheric CO2 levels.
The calculations take into account specific characteristics of different ecosystems such as vegetation growth rates, soil carbon turnover and biogeographical distribution.
From the uplands of the UK to seagrass meadows in the United Arab Emirates, WKC carries out carbon capture calculations for ecosystems all around the world.
Our carbon capture calculations are made using peer reviewed literature from academic institutions.
We utilise sequestration rates from the latest research into carbon exchange in terrestrial and marine (blue carbon) ecosystems. We apply these rates as a baseline and utilise geographic and taxonomically exact figures. We continuously review this data to keep up to date with the latest scientific developments.
Our carbon capture calculations are combined with advances in geospatial technology to give accurate estimations of the area or volume of a specific ecosystem. Typically, this will involve data captured from satellites, drones, or terrestrial and marine light detection and ranging (LIDAR) systems.
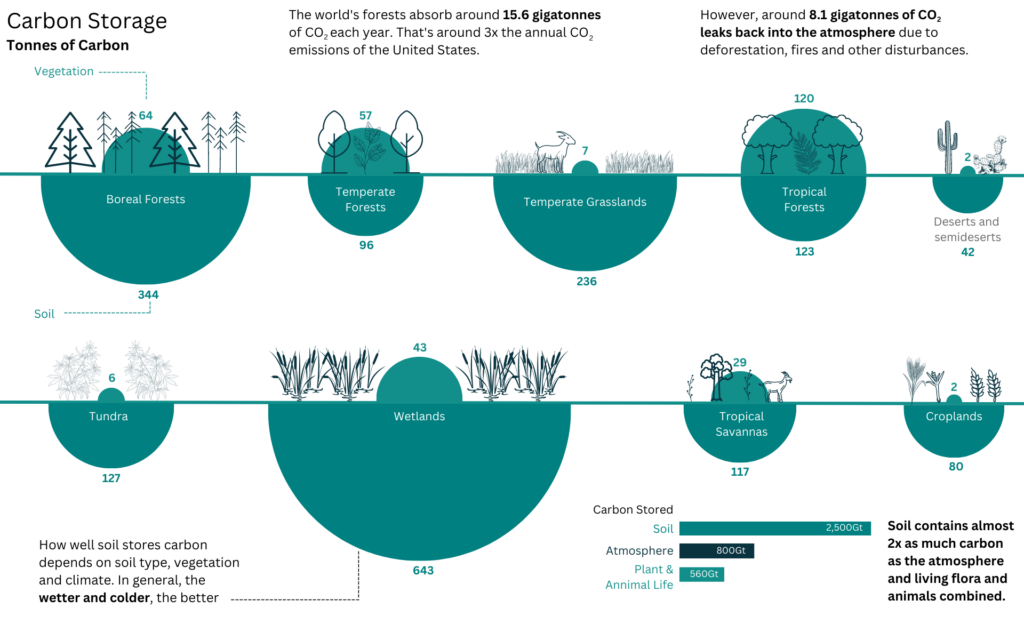
Carbon sequestration by different ecosystems, figure adapted from Visual Capitalist
Terrestrial carbon typically refers to that captured in the Earth’s forests and soils. Carbon is captured through photosynthesis and is stored as part of the natural components of ecosystems.
Planting trees is the most reliable and cost-effective way to capture carbon from the atmosphere. We have experience in carbon capture calculations for afforestation and agri-environment schemes as well as applications in forestry.
Peatlands store carbon on a massive scale. These are wetland ecosystems where carbon is preserved within organic matter due to anaerobic conditions. We are skilled in carrying out carbon capture calculations on peatlands, particularly in relation to wind farm applications, and habitat restoration schemes.
Blue carbon refers to carbon captured and stored in coastal and marine ecosystems and the ocean.
Mangrove forests, saltmarsh, and seagrass meadows sequester and store more carbon per unit area than terrestrial forests and are gaining increased global recognition for their role in mitigating climate change.
We have expertise in blue carbon capture calculations for development and planning, coastal sustainability, mangrove conservation and natural capital schemes.
Click on the links below to view the full list of our Carbon Management Services:
Carbon Capture and Sequestration
(Current page)
Carbon Reporting Resources